
| Three-phase Alternator Working Principle |
The practical application is mainly a three-phase alternator. The inner circumference of the stator core is evenly distributed with six slots, and three identical coils spaced 120 degrees apart are embedded, which are respectively called A-phase coil, B-phase coil, and C-phase coil. |

| Figure 1--Three-phase alternator stator |
At present, power plants mainly use steam turbines or gas turbines to drive generators with high rotation speed. The generator rotor has 2 magnetic poles. The structure of the generator rotor has a salient pole type (figure 2 left) and a hidden pole type (figure 2 right). Most of the two pole generator rotors adopt a hidden pole structure, and the large high speed three-phase alternators all use a hidden pole rotor. |

| Figure 2 - Salient and hidden pole rotors |
| Figure 3 shows the magnetic field state of the hidden pole rotor after the excitation power is connected. |
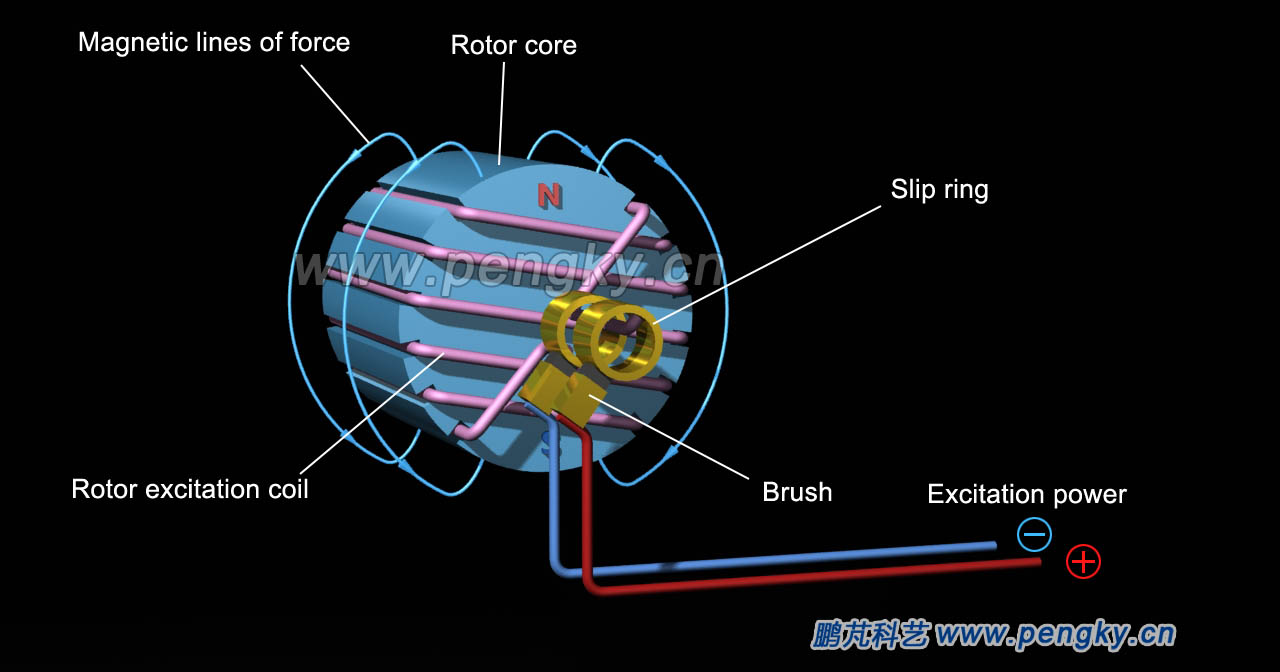
| Figure 3 - Magnetic field of a hidden pole rotor |
| The rotor is assembled to form a three-phase alternator principle model. |

| Figure 4 - Principle model of hidden pole rotor three-phase alternator |
When the rotor rotates at a constant speed, the three coils sequentially cut the magnetic lines of force, which will induce the AC electromotive force, and the amplitude change period is the same as the frequency. Since the three coils are spaced 120 degrees apart from each other, the phases of their induced potentials are also different by 120 degrees. The rotor of this model has only two poles, so the induced voltage frequency is the same as the rotor speed per second. It is a synchronous alternator. When the speed is 3000 rpm (3000r/min), the three-phase AC frequency is 50 Hertz (Hz), this two-pole synchronous generator is widely used in coal-fired power plants, gas turbine power plants and nuclear power plants, which use a steam turbine or gas turbine with a speed of 3000r/min to drive synchronous generators to generate electricity. The above principle model rotor has two magnetic poles, and the stator has six slots. The actual three-phase alternator has a plurality of slots on the stator core, and the number of slots is 3n times the number of poles (n=1, 2, 3, ...), called integer slots, and what is not an integer relationship is called a fractional slot. Multiple coils are regularly embedded in the slots to form a three-phase winding Please watch the 3D animation courseware of the three-phase alternator working principle. The animation has the output potential waveform of each phase line. |
| Three-phase alternator working principle 3D animation courseware |
 |
| Back to Previous Page |
